Erase Your Student Loan Woes With Proven Tactics
If you're ready to erase your student loan woes, follow the options and discover proven tactics that can lead you to financial freedom faster than you might expect.
Understanding the Scope of Student Loan Debt
Student loan debt has become a significant financial burden for many individuals, with the average borrower owing approximately $37,0001. This level of debt can delay major life decisions such as buying a home or starting a family. Understanding the scope of this debt is the first step in managing it effectively. By exploring various options, such as loan forgiveness programs, refinancing, and income-driven repayment plans, you can alleviate the pressure and work toward a debt-free future.
Exploring Loan Forgiveness Programs
Loan forgiveness programs are a beacon of hope for many borrowers. Programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) offer significant relief if you work in qualifying public service jobs. Under PSLF, your remaining loan balance can be forgiven after 120 qualifying payments2. Additionally, teachers and healthcare workers may find specific forgiveness programs tailored to their professions. It's essential to browse options and see these opportunities to determine eligibility and maximize benefits.
Refinancing: A Path to Lower Interest Rates
Refinancing your student loans can be a powerful strategy to reduce your interest rates. By consolidating multiple loans into a single loan with a lower interest rate, you can save money over time. Many private lenders offer competitive rates, sometimes as low as 2.5% for well-qualified borrowers3. It's crucial to compare offers from different lenders to find the best deal. Remember, refinancing federal loans with a private lender means losing federal protections and benefits, so weigh the pros and cons carefully.
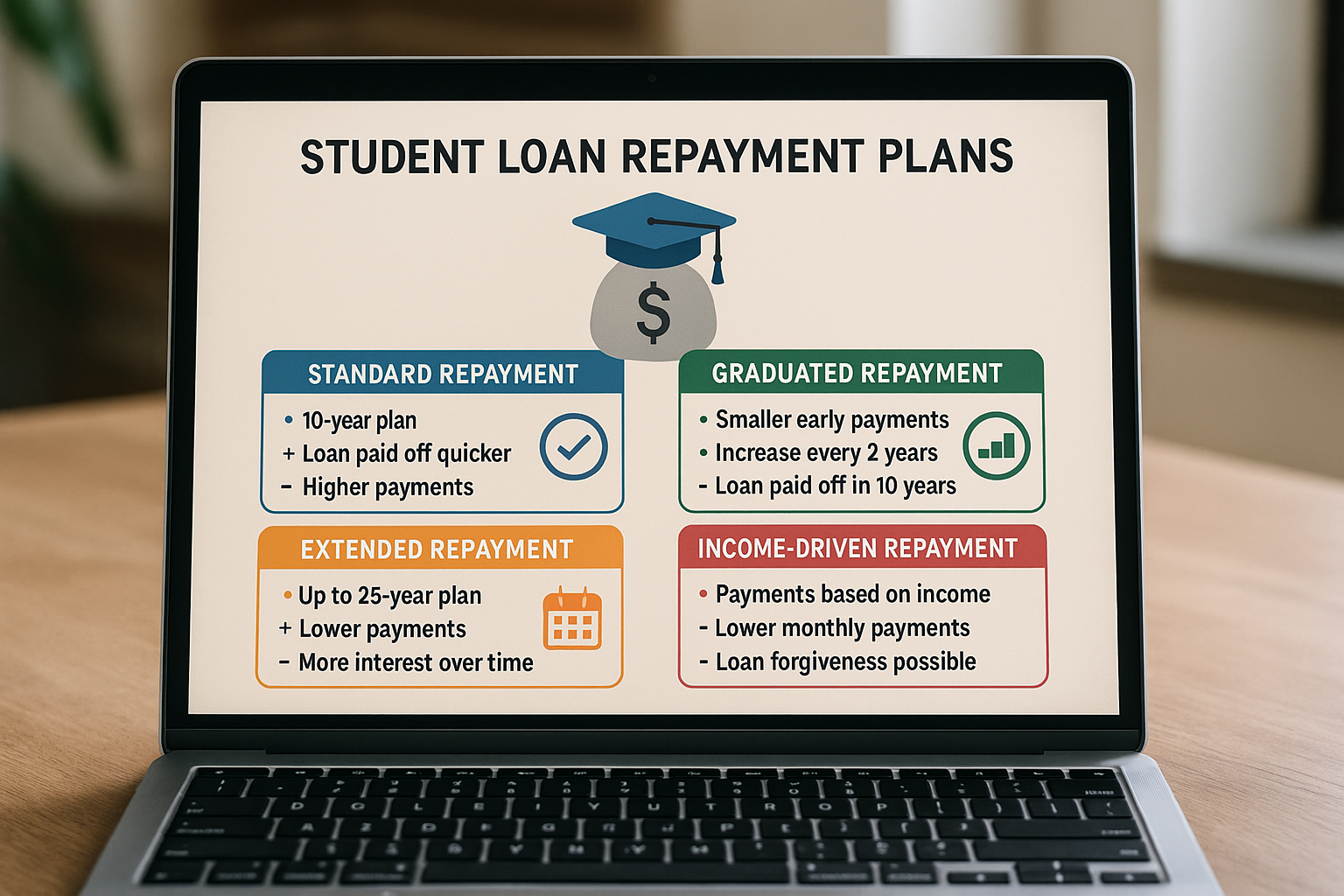
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-driven repayment (IDR) plans are an excellent option for borrowers struggling to make their monthly payments. These plans adjust your monthly payment based on your income and family size, often resulting in a lower payment. After 20 to 25 years of qualifying payments, any remaining loan balance may be forgiven4. There are several IDR plans available, including Income-Based Repayment (IBR) and Pay As You Earn (PAYE). It's beneficial to search options and find the plan that best suits your financial situation.
Budgeting and Financial Planning
Creating a realistic budget is a fundamental step in managing student loans. By tracking your income and expenses, you can identify areas to cut back and allocate more funds toward loan repayment. Financial planning tools and apps can assist in this process, offering insights into spending habits and helping you set achievable financial goals. Consulting with a financial advisor can also provide personalized strategies to manage debt effectively. Remember, every extra dollar paid toward your loan principal reduces the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Utilizing Employer Assistance Programs
Many employers now offer student loan repayment assistance as part of their benefits package. These programs can provide monthly contributions toward your loan balance, easing the repayment burden. It's worth visiting websites of prospective employers or discussing options with your current employer to explore these benefits. Some companies even offer tuition reimbursement for further education, which can be a valuable resource for reducing future educational expenses.
In summary, tackling student loan debt requires a multifaceted approach. By exploring loan forgiveness programs, refinancing options, income-driven repayment plans, and employer assistance programs, you can significantly reduce your financial burden. Additionally, effective budgeting and financial planning can accelerate your journey to becoming debt-free. As you navigate these options, consider visiting resources and specialized services to tailor solutions to your unique financial situation.